Introduction of PON
2023-01-29
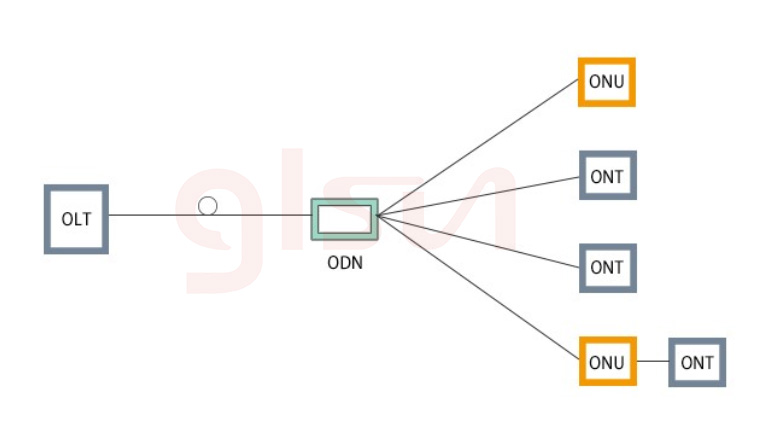
PON Passive Optical Network is a point-to-multipoint passive optical fiber access technology, which mainly includes three basic functional modules: Optical Line Terminal OLT, Optical Network Unit ONU, and Optical Distribution Network ODN.
OLT: Optical Line Terminal is simply the "upstream" operator-side equipment end of optical fiber network transmission. Its function is to communicate with the ONU on the user side through one or more ODN optical fiber distribution networks. The relationship between OLT and ONU is master and slave communication relationship, OLT manages the signaling and monitoring information from the ONU, and the OLT equipment is generally deployed in the operator's base station or the service node machine room.
ONU: Optical Network Unit locates between the ODN optical fiber distribution network and user, it belongs to the user-side equipment and is responsible for receiving the data sent by the OLT and directly providing services for the user. The network side of the ONU has an optical interface, while the user side has an electrical interface.
ODN: Optical Distribution Network is the transmission facility in optical fiber access network. It provides optical transmission channels for ONU and OLT as a physical connection between the two. ODN includes optical fiber, optical cable transfer box, optical connector (pigtail), passive optical splitter (Optical Branching Device, OBD) (optical splitter), and optical fiber connector. The components of these optical fiber networks are composed of passive optical devices, which is also the source of the name of the PON passive optical network.
PON Network Framework
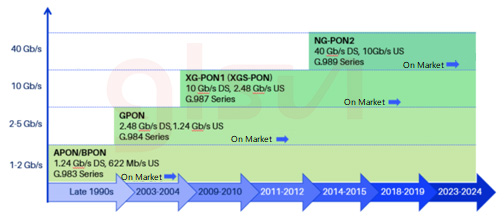
PON has developed and evolved various technical solutions in different time periods. According to the different technologies adopted, PON can be divided into APON, that is, passive optical network based on ATM technology, which was later renamed BPON broadband passive optical network; EPON is passive optical network based on Ethernet; GPON gigabit passive optical network is an extension of BPON.
PON technologies include EPON, GPON, 10G-EPON and XG-PON. Although there are great differences between different PON technologies, the main differences are in line speed, available bandwidth and working wavelength.
|
Category |
Downstream Rate (bps) |
Upstream Rate (bps) |
Downstream Wavelength (nm) |
Upstream Wavelength (nm) |
|
|
<1G |
BPON | 622M | 155M | 1490 | 1310 |
| 1G/2.5G | GPON | 2.5G | 1.25G | 1490 | 1310 |
| EPON | 1G | 1G | 1490 | 1310 | |
| 10G | 10GEPON | 10G |
1G 10G |
1577 | 1270 |
| XG-PON | 10G | 2.5G | 1577 | 1270 | |
| XGS-PON | 10G | 10G | 1577 | 1270 | |
| 40G | NGPON2 | 4X10G | 4X2.5G | 1596-1603 | 1524-1544 |
| 50G | 50G PON | 50G |
25G 12.5G |
1340-1344
|
1260-1280 1290-1310 1298-1302 |
EPON Technical Characteristics
Low operation cost and simple maintenance: Passive components are easy to lay and maintain, which can save long-term operation cost and management cost.
Provide higher transmission rate: EPON can provide up and down symmetric 1.25G rate, and can be upgraded to 10G, as well as 25G/50G in the future.
Wide range of services and easy expansion: EPON, as a point-to-multipoint network, can use a single optical module and fiber resources at the central office to serve a large number of end users, and the network is easy to expand.
GPON Technical Characteristics
Strong service support capability and full service access capability: it can provide full service access capability including E1 circuit service, ATM service, CATV, etc. It also provides voice, data and video integrated service access.
Higher bandwidth and longer transmission distance: up to 128 ONUs can be supported and the longest transmission distance can reach 60 kilometers.
PON Advantages
Low Cost: Low cost, simple maintenance, easy expansion and easy upgrade. The PON structure does not require power supply and no electronic components during transmission, so it is easy to lay, basically requires no maintenance, and saves a lot in long-term operating costs and management costs.
Pure Medium Network: The passive optical network is a pure medium network, which completely avoids electromagnetic interference and lightning effects, and is quite suitable for use in areas with harsh natural conditions.
Less Resource Usage: The PON system occupies very little resources at the central office, and the system features on low initial investment, easy expansion and high return on investment.
High Bandwidth: EPON/GPON is upgraded to 1G/2.5G-10G-25G/50G with the development of Ethernet technology.
Wide Services: Since PON adopts the point-to-multipoint access mode, the infrastructure cost of laying optical fibers between the central office and the users is shared by users, which can improve the return on investment in network construction. Compared with the method of configuring end-to-end optical fibers for each user, the PON equipment that improves services for the same number of customers is smaller and occupies less space in the central office.
Flexible bandwidth allocation, guaranteed quality of service (QoS): G/EPON system has a complete system for bandwidth allocation and guarantee, which can realize user-level SLA.
EPON and GPON are both 1Gbps-level PON, and PON has begun to evolve to 10Gbps level, and 10G PON is not the end of PON technology. With the higher network rate requirements of 25G/50G/100G, the rate of PON modules will also follow Increase.
Upgrade Path
GPON: GPON → XGPON/XGS PON → NG-PON2
EPON: EPON → 10G EPON → NG-EPON